
It can be very difficult if the number is large.
Suppose we are making a population count.
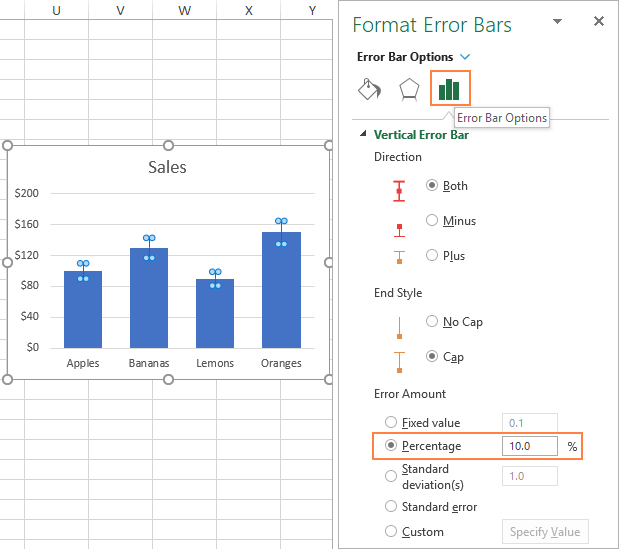
#HOW TO CALCULATE STANDARD ERROR IN EXCEL HOW TO#
But before that, let’s begin by understanding what it exactly is and how the calculation works.Īlso read: How to Calculate Variance in Excel? What is Confidence Interval? I have found some mistakes over the years which changed my test results from failing to passing.In this tutorial, we’ll learn how to calculate Confidence Interval in Excel. Even if you have a proficiency testing provider, sometimes it is best to double check their calculations. However, if you do not have a proficiency testing provider and(or) participate in interlaboratory comparisons, you may need to know how to calculate normalized error. Results outside of this range are considered nonconforming or failing.Ĭalculating normalized error is not common unless you are a proficiency testing provider. Calculated values between -1 and +1 are considered conforming or passing. Using MS Excel is the fastest way to calculate normalized error for your interlaboratory comparisons.Įvaluating the results of the normalized error equation is pretty easy. To make life easy, use the image and equation below as a guide.Īfter you have completed the first line of data with the equation, simply copy and paste cell F3 down column F for as many calculations as you need. It is fast and easy to build a spreadsheet calculator where you can perform multiple calculations very quickly. Instead of calculating normalized error the long way, try using MS Excel. After calculating normalized error, or E n, the result yielded a value of 0.09 which is between -1 and +1. 2.8ppm) and the Fluke 732B had a reference value of 9.99993365 with an uncertainty of 0.00000044V (i.e. Looking at the test data, you can see that my Fluke 732A had a value of 9.9999361V with an uncertainty of 0.000028 V (i.e. In the proficiency test, I compared my Fluke 732A DC Reference Standard to a Fluke 732B sent to me by NAPT. Need an example? I am going to calculate normalized error using data from one of my proficiency tests. If not, you may have a problem with your measurement process. If your results are satisfactory, the value of E n should be between -1 and +1. difference of measurement results) and divide it by the value calculated in the second step (i.e. Finally, use the value calculated in the first step (i.e. Next, calculate the root sum of squares for both laboratories’ reported estimate of measurement uncertainty. First, calculate the difference of the measurement results by subtracting the reference laboratory’s result from the participating laboratory’s result. If you need some help, keep reading I am going to walk you through the calculation process. E n), use the formula below as a reference.

Using the normalized error equation will allow you to evaluate the results in a manner that is acceptable to your accreditation body. If your laboratory needs to performed proficiency testing but is unable to find a PT provider, you may need to perform an interlaboratory comparison. Proficiency testing is a requirement of ISO17025. Sometimes, outliers are removed from the calculations of adjusted mean to prevent influence of excessive offsets. Normalized error is also used to identify outliers in the proficiency test results. Typically, it is the first evaluation used to determine conformance or nonconformance (i.e. Normalized error is a statistical evaluation used to compare proficiency testing results where the uncertainty in the measurement result is included. After reading this article, you should be able to calculate normalized error long-hand, using a calculator, and(or) using MS Excel. In this article, I am going to explain what normalized error is and how to calculate it. However, if you are participating in interlaboratory comparisons because there is not a proficiency test available, you may have wanted to know how to calculate normalized error to analyze your test results. When you participate in proficiency tests, the PT provider calculates normalized error for you. If you have participated in a proficiency test before, you may have noticed it in your final summary report either by name or abbreviated ‘E n.’ Calculating normalized error is common for laboratories participating in proficiency testing or interlaboratory comparisons.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
